Install on AWS
This guide will perform a complete production-ready installation in your AWS environment using AWS CDK.
This is a complex multi step process, and requires high proficiency with AWS, Node.js, and command line tools.
Medplum strives to make this as easy as possible, but despite our best efforts, it is still challenging.
If you have any questions, please contact us or join our Discord.
If you are new to AWS CDK, we strongly recommend reading Getting started with the AWS CDK.
At a high level, the process of installing Medplum on AWS includes:
- Prerequisites
- Setting up IAM permissions
- Setting up an SES account
- Configuring your domain
- Creating a config repo
- Setting up CDK
- Setting up Medplum CDK
- Running the Medplum init tool
- Deploying the CDK stack
- Bootstrapping
- Synth
- Deploy
- Deploying the Medplum app
- Building the Medplum app with your config
- Deploying the Medplum app to AWS
The resulting AWS configuration will look like the following:
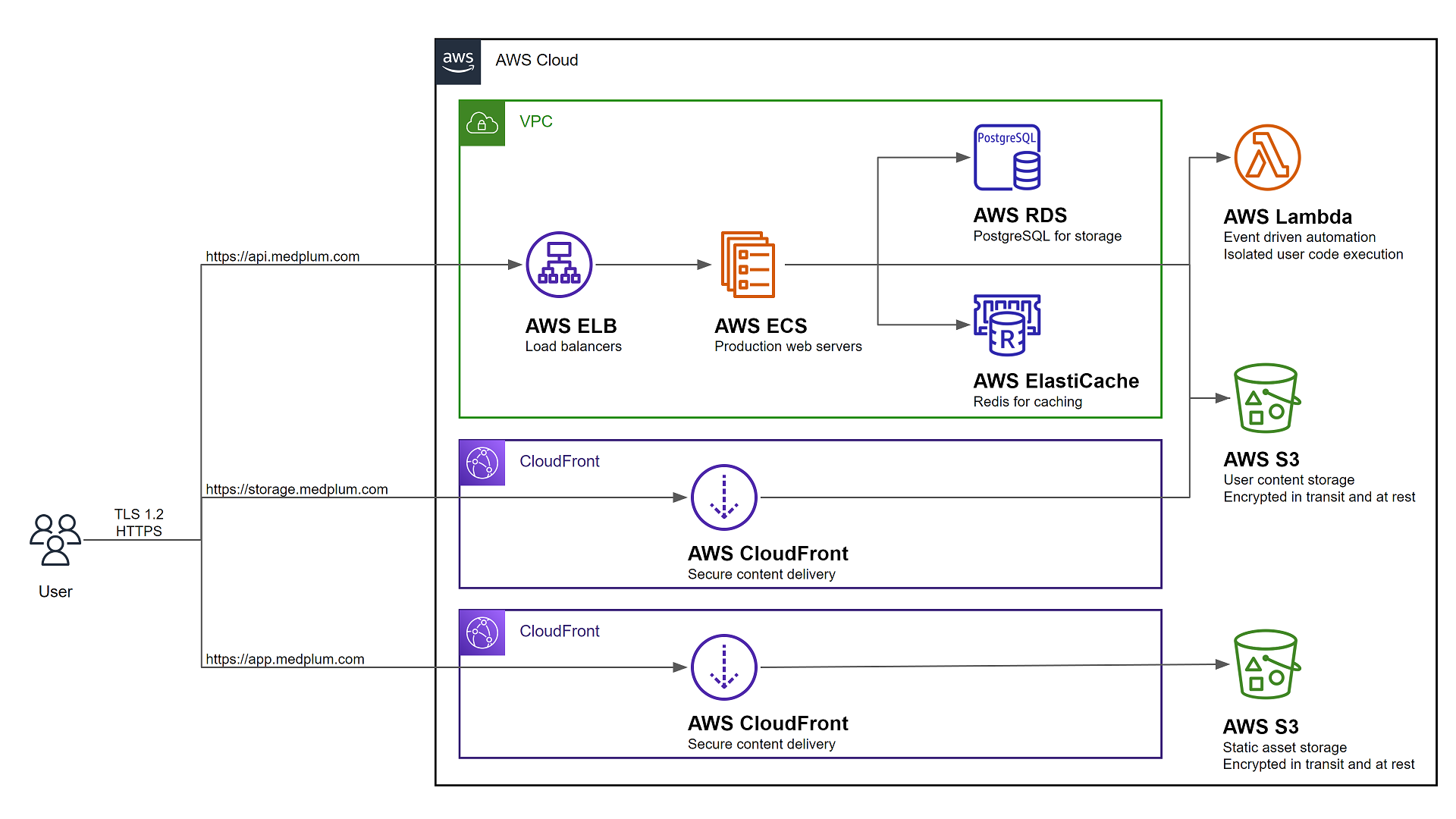
Use this video guide as you follow the instructions:
Prerequisites
AWS CLI Setup
It is recommended to setup the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) by following these instructions.
AWS Credentials Setup
AWS CLI and credentials are required by medplum aws init automate certain tasks, such as creating public key pairs.
If you have not already done so, follow these instructions to set up your AWS credentials file.
AWS Account Number
The Medplum aws init command will ask for your AWS Account Number.
If the AWS CLI and credentials are configured, then the tool will automatically identify your AWS Account Number.
If not, you can find your AWS Account Number:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console with your user name.
- In the top navigation bar, choose Support and then choose Support Center.
- Your AWS account ID (account number) appears below the top navigation bar.
AWS Permissions
You will need permission to access the following AWS services:
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
| Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) | Create a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and related security groups |
| Elasticache | Create a hosted Redis cluster for caching and task queue |
| Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) | Create a load balancer for server redundancy and high availability |
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Create service roles for the API server and bot lambdas |
| CloudFront | Securely deliver content with low latency and high transfer speeds |
| CloudWatch Logs | Create and manage log groups for server logs |
| Relational Database Service (RDS) | Create a hosted Postgres Aurora database |
| Route 53 | Create DNS entries for the services |
| Simple Storage Service (S3) | Host static web content, store and retrieve dynamic user content for file attachments |
| Secrets Manager | Store encrypted secret configuration details such as database credentials |
| Systems Manager (SSM) | Store configuration details |
| Web Application Firewall (WAF) | Protect your web applications or APIs against common web exploits and bots |
Configure your name servers
Medplum strongly recommends configuring your domain to use Amazon's Route 53 as your custom DNS name server. This will make it much easier to set up SSL certificates for the Medplum App and Medplum Binary Storage.
If you choose not to go this route, you will be responsible for setting up your own SSL certificates.
Setup SES
It is strongly recommended to setup an SES email address with production access, meaning that it can send email to any email recipient. Email is used to verify identities, send login instructions, and handle password reset requests.
Follow the Creating and verifying identities in Amazon SES guide to register an email address for system generated emails.
Choose an environment name
Throughout this document, instructions will refer to an "environment name". This environment name is used in multiple places, for example an environment named demo will result in:
- As part of config file names (i.e.,
medplum.demo.config.json) - As the base of CloudFormation stack names (i.e.,
MedplumDemo) - AWS Parameter Store keys (i.e.,
/medplum/demo/...)
If you plan to deploy multiple Medplum clusters, you may want to consider a naming strategy.
For example:
| Env Name | Config file name | CloudFormation stack name | Parameter Store prefix |
|---|---|---|---|
| prod | medplum.prod.config.json | MedplumProd | /medplum/prod/... |
| staging | medplum.staging.config.json | MedplumStaging | /medplum/staging/... |
| test | medplum.test.config.json | MedplumTest | /medplum/test/... |
| alice | medplum.alice.config.json | MedplumAlice | /medplum/alice/... |
| bob | medplum.bob.config.json | MedplumBob | /medplum/bob/... |
Medplum configuration files and environment names are quite flexible, but it is always recommended to be consistent and stay organized.
Setup a config repo
Create your config repo
Medplum recommends creating a separate git repository and npm project to manage your CDK infra-as-code. This repository will only contain JSON configuration files.
mkdir my-medplum-cdk-config
cd my-medplum-cdk-config
npm init -y
Medplum recommends pushing this git repository to your source control provider such as GitHub or GitLab.
Add CDK dependencies
If you have not already done so, add the common AWS CDK dependencies. This includes all of the base CDK capabilities and constructs.
npm i aws-cdk-lib cdk constructs
Add Medplum dependencies
Add the Medplum CDK and CLI dependencies. This includes the Medplum CDK construct.
npm i @medplum/cdk @medplum/cli
Add cdk.json��
Create a new file called cdk.json with the following contents:
{
"app": "node node_modules/@medplum/cdk/dist/cjs/index.cjs"
}
Run the init tool
Most AWS resources are automatically created using CDK, but some either cannot or are not recommended. Use the medplum aws init command to setup those resources and build the Medplum CDK config file.
npx medplum aws init
Then follow the prompts.
Upon completion, the tool will:
- Generate a Medplum CDK config file (i.e., medplum.demo.config.json)
- Optionally generate an AWS CloudFront signing key
- Optionally request SSL certificates from AWS Certificate Manager
- Optionally write server config settings to AWS Parameter Store
Make note of the CDK config file name.
See Config Settings for more details on each of the individual configuration settings.
(Optional) Validate Certificates
If you are using Route 53 as your DNS service, we recommend you select dns method for validating domain ownership.
Then, follow these instructions from AWS to finish the validation process.
CDK Bootstrap
Bootstrapping is the process of provisioning resources for the AWS CDK before you can deploy AWS CDK apps into an AWS environment.
Run CDK bootstrap:
npx cdk bootstrap -c config=medplum.demo.config.json
Learn more about bootstrapping: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/latest/guide/bootstrapping.html
CDK Synth
The synth step catches logical errors in defining your AWS resources.
Run CDK synth:
npx cdk synth -c config=medplum.demo.config.json
CDK Diff
Use the diff command to see how it will change your AWS resources.
Run CDK diff:
npx cdk diff -c config=medplum.demo.config.json
CDK Deploy
When you are ready to actually execute the CDK configuration, use the deploy command.
Run CDK deploy:
npx cdk deploy --all -c config=medplum.demo.config.json
Note that you may receive warnings about changing security details. This is normal and expected anytime CDK makes changes to VPC, IAM, and other security features.
Update Bucket Policies
When deploying to any region other than us-east-1, there is one additional step. AWS CloudFront needs access to S3 buckets. At present, this is not possible entirely within CDK.
This is due to cross-region circular dependencies:
- An S3 bucket in your primary region
- A CloudFront distribution in
us-east-1, because CloudFront distributions must always be inus-east-1 - Updated S3 bucket policy that references the CloudFront distribution
See this Github issue for more details.
The Medplum CLI includes a command to update the bucket policy automatically:
npx medplum aws update-bucket-policies [env name]
For example:
npx medplum aws update-bucket-policies demo
You can use the --dryrun option to preview the changes:
npx medplum aws update-bucket-policies [env name] --dryrun
Deploy the app
Historically this step required building from source. You can now deploy the app from prebuilt images.
Use the Medplum CLI to deploy the app:
npx medplum aws deploy-app [env name]
For example:
npx medplum aws deploy-app demo
Advanced
Bot Lambda Layer
Optional: If you intend to use Medplum Bots, you will need an AWS Lambda Layer.
At present, the bot layer must be built from source. See Clone the repo.
After you successfully clone the Medplum repo, you can use the deploy-bot-layer.sh script to build and deploy the Lambda Layer:
git clone https://github.com/medplum/medplum.git medplum
cd medplum
./scripts/deploy-bot-layer.sh
See the Medplum Bot Layer guide to learn more.
Ongoing
Upgrade AWS infrastructure
Use CDK to upgrade the infrastructure.
First run cdk diff to check for changes:
npx cdk diff -c config=medplum.[env name].config.json
Then run cdk deploy to apply changes:
npx cdk deploy -c config=medplum.[env name].config.json
Upgrade the app
Use the Medplum CLI to upgrade the app. This will upgrade your app to the latest version.
npx medplum aws update-app [env name]
For example:
npx medplum aws update-app demo
Upgrade the server
Use the Medplum CLI to upgrade the server. This will upgrade your server to the latest version.
npx medplum aws update-server [env name]
For example:
npx medplum aws update-server demo
Troubleshooting
Cannot assume role
You may receive a warning such as:
current credentials could not be used to assume 'arn:aws:iam::[ACCOUNT_ID]:role/cdk-hnb659fds-file-publishing-role-[ACCOUNT_ID]-us-west-2',
but are for the right account. Proceeding anyway.
First, make sure that the specified role exists in your AWS account. If it does not exist, make sure that you ran the cdk bootstrap command.
Next, make sure that your AWS account has permission to assume the role via sts:AssumeRole. You may need to add an IAM policy to add permission.
{
"Sid": "assumerole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["sts:AssumeRole", "iam:PassRole"],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:iam::*:role/cdk-*"]
}
"IAM Full Access" is not enough! The IAM Full Access policy does not include sts:AssumeRole.
Try verbose mode
All CDK operations support verbose logging by adding the --verbose flag. Verbose logging can often reveal hints about confusing behavior.
npx cdk synth --verbose -c config=medplum.demo.config.json